《Matching the Blanks: Distributional Similarity for Relation Learning》
目标:基于大量未标注语料,训练一个relation表征的模型
input:relation statement(x, s1, s2)
output:relation representation: 一个稠密向量,使得两个关系越接近,两个关系的表征向量点积值越大
bert-based architecture:
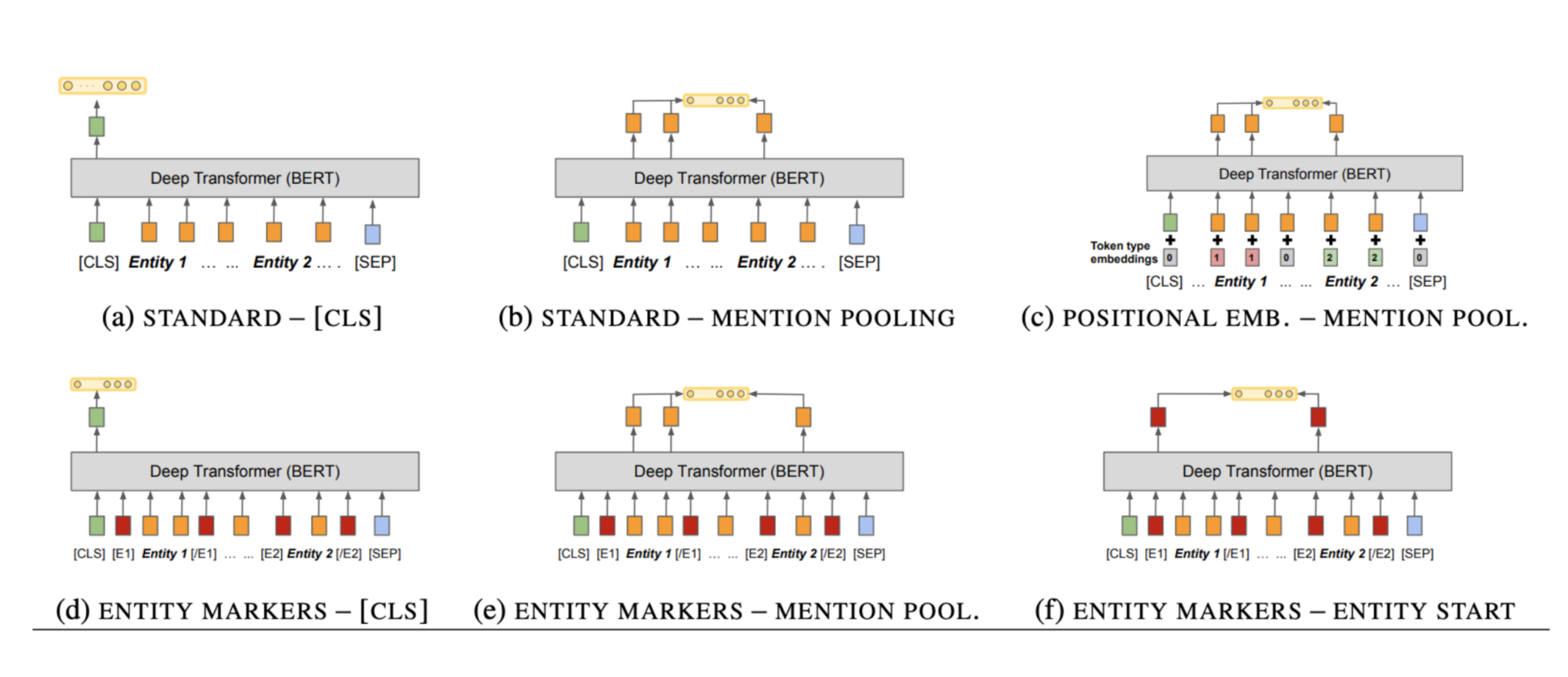
预训练
- There is high degree for redundancy in web text, relation between tow entity is likely to be stated multiple times
- 两个不同的句子中,如果包含相同的实体对,这个实体对在两句话中大概率表示相同的relation
- 两个不同的句子中,如果包含不同实体对,这两个实体对大概率表示不同的relation
- 例子:

- 结构:
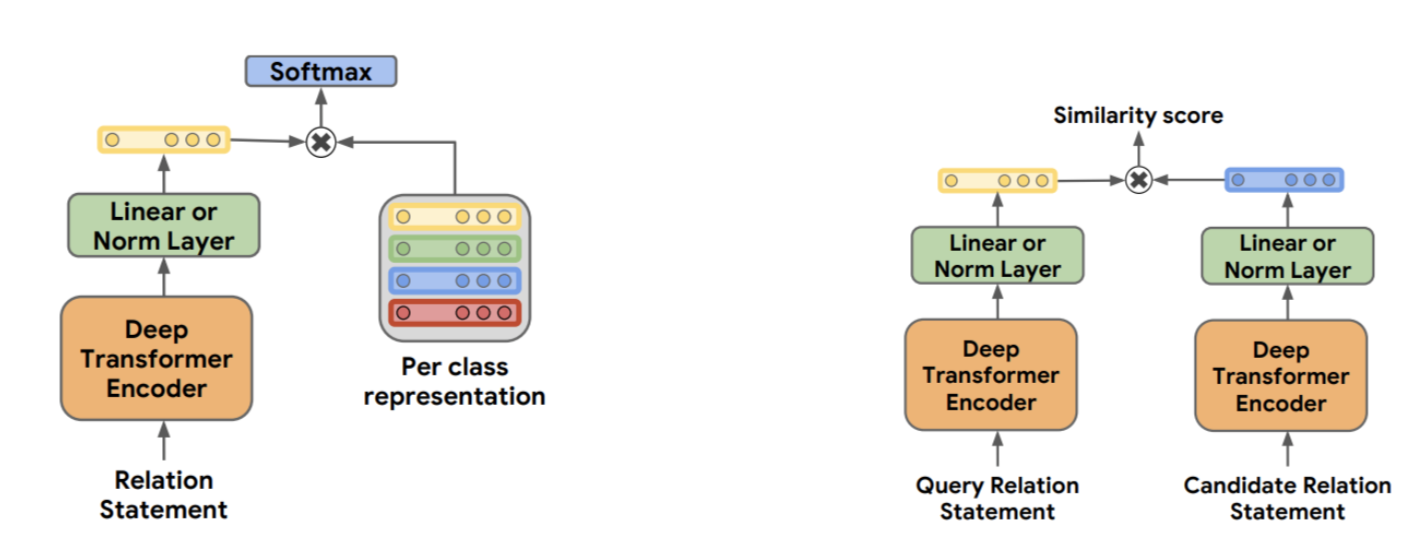
实验细节
- 采用维基百科数据,用google cloud natural language api做实体链接
- 以α = 0.7的概率将entity mention 替换成[BLANK]
- negative sampling with relations share one entity
- 生成了600M的实体对,正负样本1:1
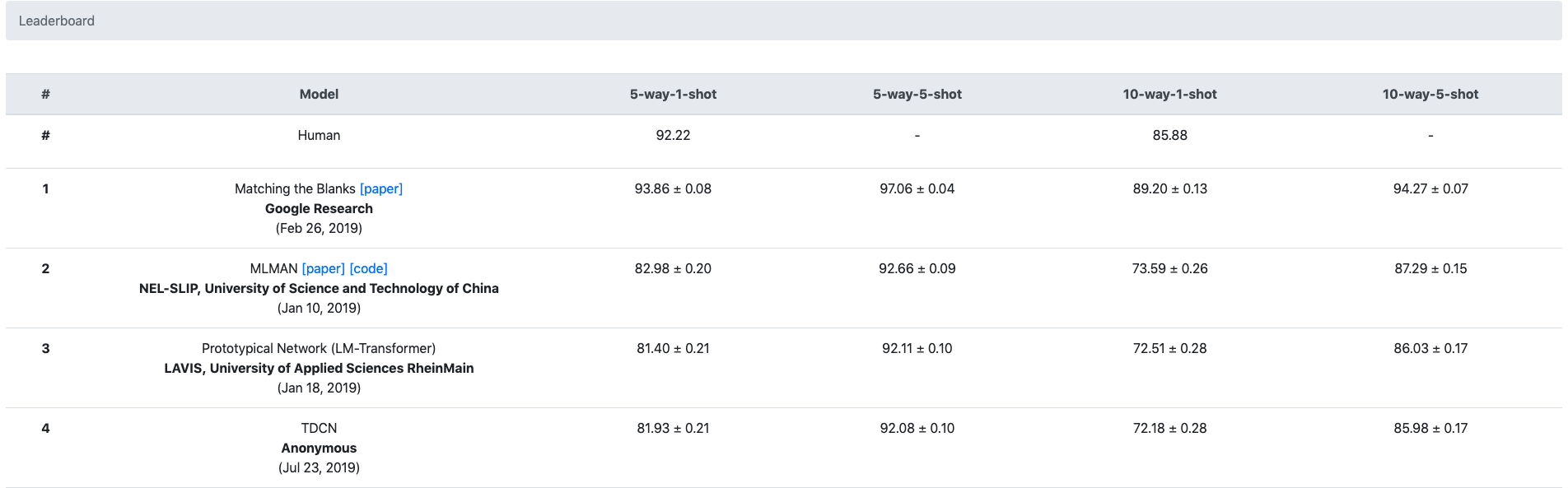
实验结果
- 在supervised training任务下,有细微提高,可以提高模型收敛速度
- 在Few Shot任务下,提高明显:
启发
- 想办法在未标注数据中提取有用信息,在大规模数据上做预训练,然后在标注任务中做fine-tune是提升任务效果的比较好的方案(BERT,GPT…)。这种方案相比在给定的标注数据下,优化模型的结构,往往提升更多
- 我们爬取了百度百科的数据,可以利用百科网页的链接+简单的实体链接技术,在百度百科的数据上预训练一个中文关系表征模型
- 可以基于关系表征模型做聚类,用来发现新的关系,进而做一个schema-free的抽取系统
《Matching the Blanks: Distributional Similarity for Relation Learning》